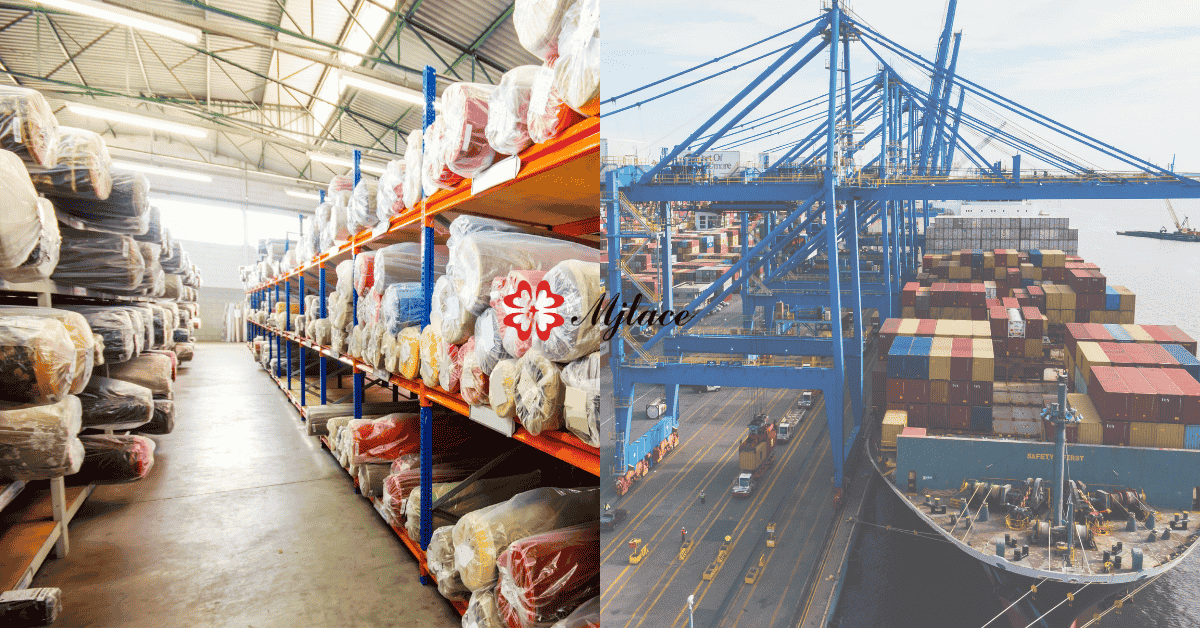
A Complete Guide to Global Textile Shipping, Customs, and Supply Chain Management
In global lace and textile sourcing, logistics is not just transportation—it is a strategic part of cost control, delivery reliability, and brand reputation.
For fashion brands, garment manufacturers, and sourcing agents, understanding how lace fabrics move from factory to warehouse is essential to avoiding delays, unexpected costs, and compliance risks.
This guide explains the entire importing and logistics process for lace fabrics, from factory pickup to final delivery, covering shipping methods, customs clearance, documentation, packaging, lead time planning, and common mistakes buyers should avoid.
Why Logistics Matters in Lace Fabric Importing
Lace fabrics are high-value, detail-sensitive textiles. Compared to basic woven fabrics, lace presents unique logistics challenges:
-
Lightweight but high cubic volume
-
Easily deformed, wrinkled, or damaged
-
Often shipped in wide widths or extra-long rolls
-
Frequently customized with color, pattern, or embroidery
-
Time-sensitive for seasonal fashion collections
A well-managed logistics process helps buyers:
-
Control landed cost
-
Protect fabric quality
-
Meet production schedules
-
Reduce supply chain risks
Common Shipping Methods for Lace Fabrics
1. Sea Freight (FCL & LCL)
Best for:
-
Large volume orders
-
Regular bulk replenishment
-
Cost-sensitive projects
Options:
-
FCL (Full Container Load): Best for stable production orders
-
LCL (Less than Container Load): Suitable for smaller trial orders
Pros:
-
Lowest cost per meter
-
Stable for long-distance shipping
Cons:
-
Longer transit time
-
Port congestion risks
Typical transit time:
-
Asia → Europe: 30–40 days
-
Asia → USA: 25–35 days
2. Air Freight
Best for:
-
Urgent production deadlines
-
High-value lace fabrics
-
Sampling and color approvals
Pros:
-
Fast delivery (3–7 days)
-
Lower risk of humidity damage
Cons:
-
Higher cost
-
Volume limitations
3. Express Courier (DHL / FedEx / UPS)
Best for:
-
Sample books
-
Color lab dips
-
Small development orders
Pros:
-
Door-to-door service
-
Simple documentation
Cons:
-
Not suitable for bulk orders
-
Cost increases rapidly by weight
Lace Fabric Packaging Standards
Proper packaging is critical to preserving lace quality during transit.
1. Common Packaging Methods
-
Roll packing (most common)
-
Folded packing (for embroidery lace panels)
-
Tube rolling for extra-wide lace
-
Moisture-proof wrapping
2. Packaging Materials
-
PE film inner wrap
-
Kraft paper or foam layers
-
Cartons or woven bags
-
Desiccants for sea freight
Poor packaging may cause:
-
Fabric deformation
-
Color transfer
-
Edge damage
-
Mold in humid conditions
Essential Import Documents for Lace Fabrics
Buyers should always confirm document accuracy before shipment.
1. Basic Shipping Documents
-
Commercial Invoice
-
Packing List
-
Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
-
Certificate of Origin
2. Textile-Specific Documents
-
Fiber content declaration
-
HS code confirmation
-
Testing reports (if required)
-
REACH / OEKO-TEX statements (for EU markets)
Incorrect documentation may lead to:
-
Customs delays
-
Additional inspection
-
Unexpected duties or penalties
HS Codes and Customs Classification
Correct HS code classification is critical for lace fabrics.
Typical lace-related HS codes include:
-
Knitted lace fabrics
-
Embroidered textiles
-
Chemical lace (Guipure)
-
Polyester lace fabrics
Why this matters:
-
Determines import duty rate
-
Affects compliance requirements
-
Impacts clearance speed
Always verify HS codes with:
-
Supplier
-
Customs broker
-
Local customs authority
Customs Clearance Process Explained
1. Standard Clearance Steps
-
Arrival at port or airport
-
Document submission
-
Duty & tax calculation
-
Inspection (if selected)
-
Cargo release
2. Common Clearance Risks
-
Incorrect declared value
-
Mismatch between invoice and packing list
-
Missing textile composition details
-
Non-compliant labeling
Experienced lace suppliers often assist buyers by:
-
Pre-checking documents
-
Advising on HS codes
-
Preparing compliance files in advance
Lead Time Planning for Lace Fabric Imports
A realistic lead time includes:
-
Sample approval
-
Production time
-
Packaging
-
Domestic transport
-
International shipping
-
Customs clearance
-
Local delivery
Typical Reference Timeline
| Stage | Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Sampling & approval | 7–14 days |
| Production | 15–30 days |
| Sea shipping | 25–40 days |
| Customs & delivery | 5–10 days |
Best practice:
Always build buffer time for peak seasons and holidays.
Cost Structure of Lace Fabric Importing
Understanding total landed cost helps avoid budget overruns.
Cost Components
-
Fabric unit price
-
Packaging cost
-
Inland transport
-
International freight
-
Insurance
-
Import duty & VAT
-
Local handling fees
A low fabric price can quickly lose advantage if logistics is poorly planned.
Common Mistakes Buyers Should Avoid
-
Choosing shipping method based on price only
-
Ignoring humidity protection
-
Underestimating customs clearance time
-
Not confirming HS codes in advance
-
Mixing lace types in one shipment without clear labeling
Professional suppliers help buyers avoid these mistakes proactively.
How Reliable Lace Suppliers Support Logistics
A professional lace manufacturer does more than produce fabric.
They also support buyers with:
-
Export-compliant packaging
-
Accurate documentation
-
Logistics consultation
-
Flexible shipping options
-
Risk-aware lead time planning
This level of support is especially important for:
-
International brands
-
New sourcing teams
-
Buyers entering new markets
Conclusion: Logistics Is a Competitive Advantage
In the lace and textile industry, logistics excellence directly affects product quality, delivery speed, and buyer confidence.
By understanding importing procedures, choosing the right shipping methods, and working with experienced suppliers, buyers can transform logistics from a cost burden into a strategic advantage.
Whether you are sourcing lace for fashion, bridalwear, or high-end garments, a transparent and well-managed logistics process is essential for long-term success.