Lace, this delicate and complex fabric, has always held a pivotal position in the fashion world. Whether it's haute couture gowns, luxury lingerie, or modern everyday wear, lace adds unique charm and texture to designs. However, the dyeing process for lace is far more complex than that of ordinary textiles. Its intricate openwork structure and diverse fiber composition place extremely high demands on dyeing techniques. This guide will delve into the entire dyeing process of lace, combining professional dyeing and finishing knowledge to reveal the secrets of producing high-quality lace fabrics.
Lacedyeing: What's so special about it?
Lace is typically made of cotton, silk, nylon, polyester, or blended fibers, characterized by its intricate openwork patterns and complex structure. This hollow structure makes fluid dynamics, temperature control, and tension management crucial during the dyeing process. Unlike plain or knitted fabrics, lace is more prone to the following problems during dyeing:
-
Color streaks and unevenness: Due to uneven structure, dye penetration is uneven.
-
Structural deformation: It is prone to stretching or damage under high temperature or mechanical stress.
-
Loss of detail: Over-processing can lead to blurred details.
-
Strength loss: Some fibers may lose tensile strength during the dyeing process.
Understanding these unique challenges is the first step to mastering lace dyeing techniques.
A complete breakdown of lace dyeing techniques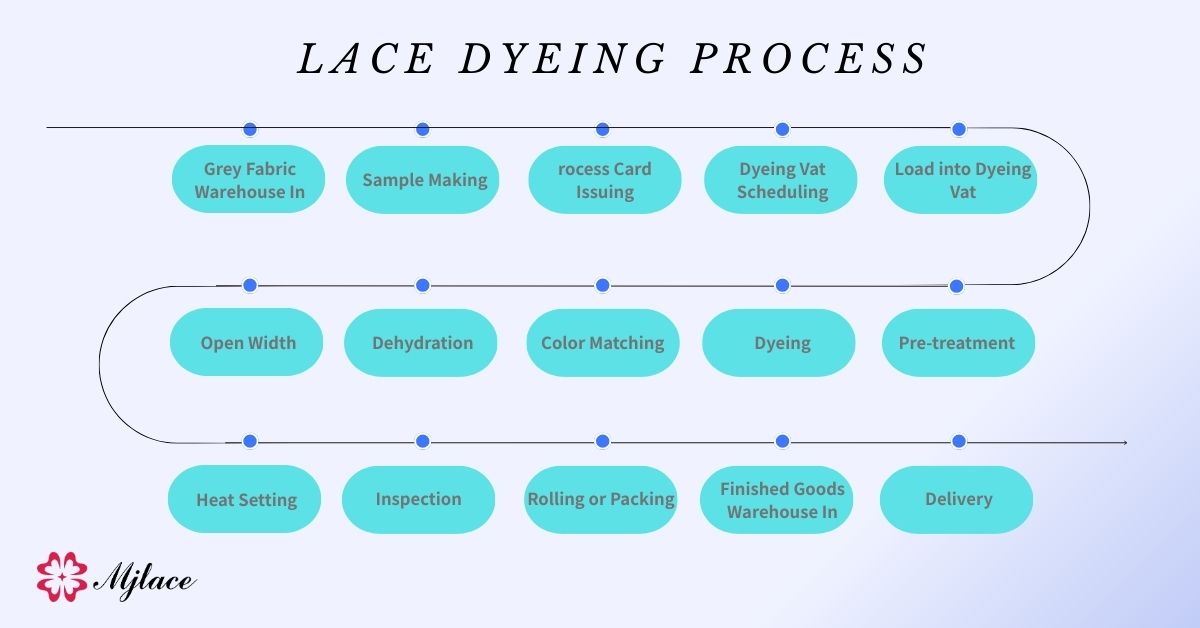
Preparations before staining
Inspection and classification of grey fabric
Once the gray lace fabric arrives at the warehouse, it will undergo rigorous inspection by technical experts. Key parameters recorded include:
-
Fiber composition ratio (directly affects dye selection)
-
Fabric weight (GSM) and thickness (affect dyeing time and temperature)
-
The density of the perforation pattern (affects dye penetration)
-
Fabric width and roll length (based on production plan)
-
The whiteness and cleanliness of gray fabrics (will affect the final color tone).
Different lace materials require different pretreatment methods, which are fundamental steps to ensure dyeing quality.
Laboratory staining (sampling): the starting point for color determination.
Laboratory dyeing of lace is more complex than dyeing ordinary fabrics and requires consideration of the following factors:
Fabric color matching: Laboratory color matching samples must use gray fabric from the same batch and specification as the bulk fabric. Even slight differences can lead to color variations.
Structural factors: The hollow and solid parts of lace absorb dye at different rates. This characteristic must be fully considered during laboratory dyeing, and sometimes it is necessary to adjust the dye concentration or add a penetrant.
Surface treatment simulation: If the final product requires surface treatments such as waterproofing, antistatic properties, or softening, these treatments must be performed during the laboratory immersion stage, as surface treatments can significantly alter the color appearance.
Multi-light source color evaluation: Lace is often used in high-end fashion. Color consistency must be checked under multiple light sources (daylight D65, TL84, etc.) to avoid metamerism ("color flipping").
Laboratory sample preparation: Professional printing and dyeing factories will prepare two samples, A and B, for customers to choose from. Only samples with a color fastness of level 4 or above and accurate color matching can enter the mass production stage.
Second stage: Preprocessing
The purpose of lace pretreatment is to remove residual grease, paste and impurities during the production process without damaging its fine structure.
Lace-specific pretreatment solution:
-
Gentle desizing: Low or medium temperature desizing process is used to avoid damage to the lace structure caused by high temperature.
- Precise pH control: Maintain a uniform pH value on the fabric surface to prevent uneven dyeing in subsequent processes.
Improper pretreatment can lead to uneven dyeing and poor color fastness, which is especially important for complex lace.
Dyeing Process and Dye Selection
Dye Selection Principles
The choice of lace dye depends on the fiber composition:
-
Nylon/silk lace: Suitable for acid dyes. Control the pH value at 5-6 and dye at 100℃ for 40-60 minutes.
-
Polyester lace: Suitable for disperse dyes that require high temperature and high pressure (HTHP) dyeing (130-135°C).
-
Cotton lace: Suitable for reactive or direct dyes, but the amount of alkali used must be strictly controlled.
-
Blended fiber lace: may require multiple dyeing processes using different types of dyes, which makes the process design more complex.
Selection of dyeing machine
Considering the properties of lace, the following dyeing machines are recommended:
Overflow dyeing machine: The dye flow is gentle and suitable for most types of lace. Low tension minimizes stretching and deformation.
Warping and dyeing machine: Suitable for thin, structurally stable lace, enabling mass production. Care should be taken to avoid lateral eccentricity or batch-to-batch variations.
Airflow dyeing machine: a new technology that uses air instead of water to transport fabrics, especially suitable for high-end lace and deformable fabrics. This equipment has the advantages of low energy consumption and significant water saving.
Special considerations for lace dyeing
Temperature control: Slow heating is crucial to prevent sudden thermal shock from causing the lace to shrink or deform.
Dye ratio management: To ensure that the dye penetrates evenly into the complex lace structure, a slightly higher dye ratio may be required.
Flow rate control: The flow rate of the dye solution must be carefully adjusted—it must be ensured that the dye circulates evenly, but not too fast to avoid damaging the lace.
Additives:
-
Penetrating agent: helps the dye penetrate into the denser areas of the lace.
-
Leveling agent: Prevents streaks and ensures uniform color.
-
pH buffer solution: maintains the stability of the dye bath.
-
Lubricant/fabricant (in shower gel): Reduces friction and protects the lace structure.
Fourth stage: Post-staining treatment and fixation
Dyed lace needs to be thoroughly rinsed to remove unfixed dye before it is fixed to improve colorfastness.
Special lace fixing technology:
-
A gentle setting agent: to avoid affecting the feel of the lace.
-
Low-temperature color fixing: to prevent high temperatures from damaging the fibers.
-
Rinse thoroughly: Ensure all chemical residues are completely removed.
For lace requiring special functions (such as waterproofing and stain resistance), functional finishing can be done at this stage.
Common lace dyeing defects and solutions
Structural distortion
Appearance: The lace pattern is deformed and the size is unstable.
Solution
-
Use low-tension staining equipment.
-
Control the heating rate to ensure it does not exceed 1.5°C per minute.
-
During the heat setting process, both overfeed and tension were precisely controlled.
Uneven dye penetration
Performance: Lace will present different color tones depending on its thickness.
Solution:
-
Add a special penetrant.
-
Extend the dye penetration time.
-
Adjust the wine circulation method.
Insufficient colorfastness
Characteristics: The color fades noticeably after washing.
Solution:
-
Choose dyes with high fastness.
-
Optimize the fixed process.
-
Make sure to thoroughly remove any sediment and rinse thoroughly.
Loss of definition
Appearance: The edges of the delicate lace pattern are blurred.
Solution:
-
Control the dye concentration.
-
Shorten the staining time.
-
Use dyes with smaller molecular weights.
Heat setting: The final shape of lace
Heat setting is a crucial step that determines the final quality of lace, requiring a precise balance of temperature, speed, and tension.
Key parameters for heat setting of lace:
-
Temperature: Set according to fiber composition, usually 10-20°C lower than standard fabric.
-
Machine speed: Lower speeds ensure complete heating and shaping.
-
Overfeeding: Appropriate overfeeding can maintain the softness of the lace.
-
Width: Precisely controlled to prevent stretching and deformation.
Precautions for heating and shaping:
-
Regularly inspect the pins/plates to prevent scratches.
-
Dark and light pigments should be stored separately to prevent color mixing.
-
Control the airflow uniformity within the tenter frame to prevent color differences between the left and right sides.
-
Monitor fabric weight (GSM) and shrinkage rate to ensure compliance with regulations.
Quality Inspection Standards
High-quality lace must undergo rigorous testing:
Visual inspection:
-
Color uniformity (level 4 or above)
-
Pattern integrity without distortion
-
The surface is clean and free of stains.
-
The edges are neat and intact.
Physical fitness test:
-
Color fastness (washability, rubbing resistance, perspiration resistance)
-
Dimensional stability (shrinkage rate)
-
tensile strength
-
Precision of fabric weight (GSM) and width
Functional testing:
-
Verify specific features (e.g., waterproofing).
-
Satisfy sensory requirements
-
Environmental and safety performance testing (e.g., Oeko-Tex)
Sustainable dyeing process for lace
Modern lace dyeing is increasingly focused on environmental responsibility and sustainability:
-
Environmentally friendly dyes: We use environmentally friendly dyes that meet standards such as Oeko-Tex.
-
Water-saving technologies: Low liquor ratio dyeing and air dyeing techniques are used.
-
Energy recovery: Implement heat recovery systems to reduce energy consumption.
-
Chemical management: Optimize chemical formulations to minimize usage.
-
Wastewater treatment: We employ advanced water treatment systems to ensure that emissions comply with relevant regulations.
In conclusion
Lace dyeing is an exquisite craft that blends art and technology. From fiber selection to final shaping, every step requires a perfect combination of expertise, precision equipment, and extensive experience. Understanding these complex processes not only helps designers choose more suitable fabrics but also assists manufacturers inoptimizing production to create beautiful, durable, and high-quality lace products.
With technological advancements and a deepening understanding of sustainable development, lace dyeing techniques will continue to evolve, bringing us more high-end fabrics with rich colors, outstanding textures, and environmental friendliness. Whether for luxury fashion or everyday wear, meticulously dyed lace will add infinite brilliance to the fashion world with its unique charm.
Professional advice: When choosing a lace supplier, don't just look at the colors and prices; also examine their dyeing processes, quality control systems, and sustainable development practices. Only suppliers with comprehensive professional capabilities can consistently provide high-quality lace products.